The Link Between Food & Mental Health
August 26, 2025
What we eat affects how we feel, physically, emotionally, and mentally. The relationship between diet and mental health is complex, but research is clear: a nutrient-rich, balanced diet can help stabilize mood, support brain function, and even ease symptoms of anxiety and depression.
At Sage Health, we believe in treating the whole person, body and mind. That’s why our care approach includes nutrition counseling for seniors from licensed dietitians who understand how deeply food choices affect emotional wellness.
Want to take control of your health? Become a patient at Sage Health and meet with our expert nutritionists and dietitians.

Best Foods for Mental Health
A healthy diet for mental health isn’t about avoiding food—it’s about including the right ones. Below are categories of foods proven to support better mood, brain function, and emotional well-being.
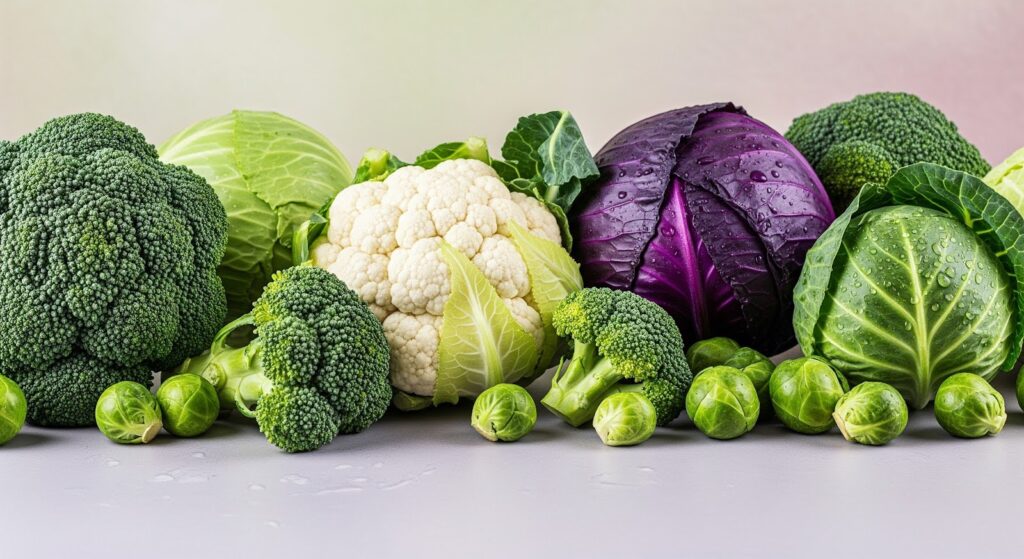
1. Cruciferous Vegetables
List: Broccoli, cauliflower, cabbage, brussels sprouts, kale, arugula
Benefits in Mental Health:
These vegetables are packed with antioxidants and fiber, which help reduce inflammation and support a healthy gut—both key to brain health. They’re also rich in folate, which supports neurotransmitter function.

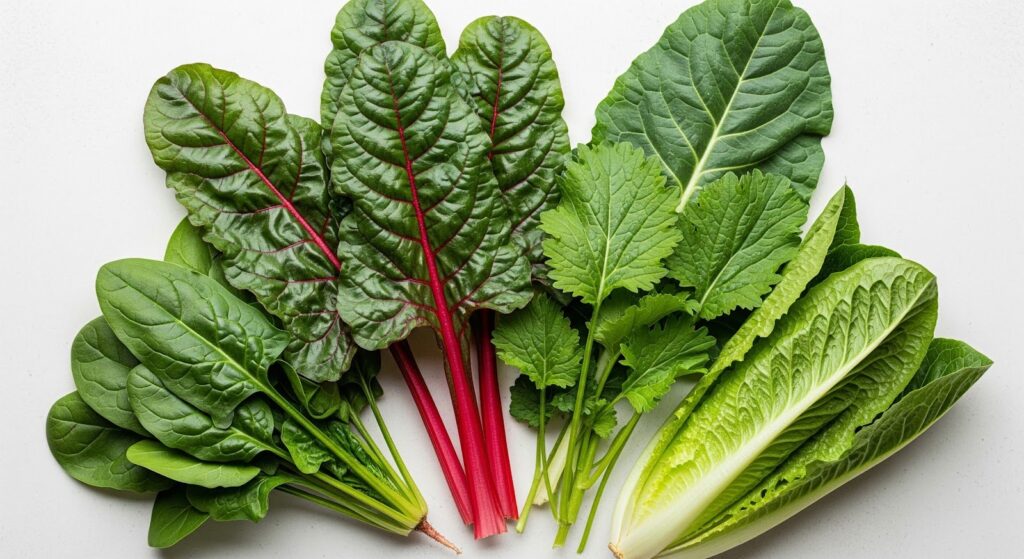
2. Leafy Greens
List: Spinach, swiss chard, collard greens, mustard greens, romaine lettuce
Benefits in Mental Health:
Leafy greens are high in magnesium, which plays a vital role in mood regulation. Low magnesium levels have been linked to depression and anxiety.

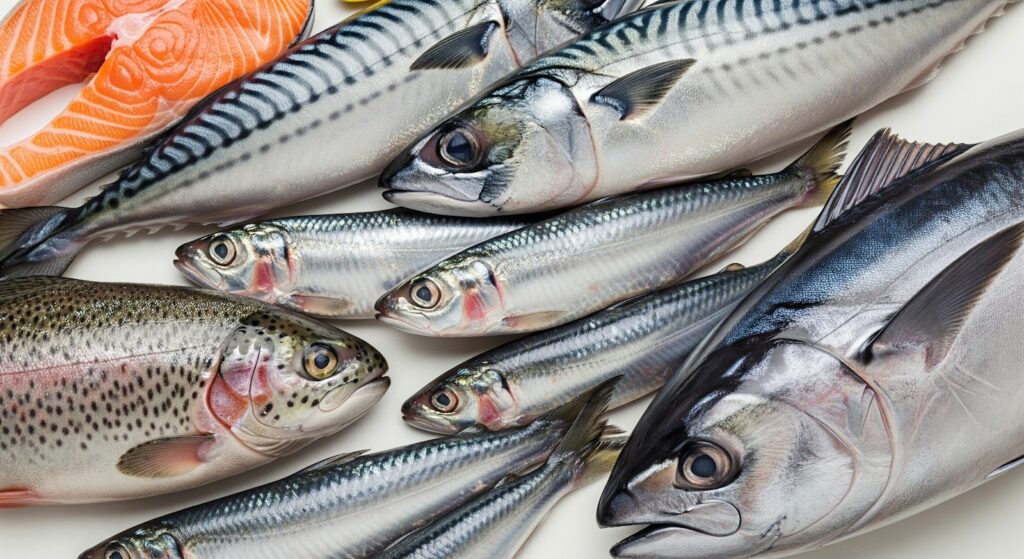
3. Fatty Fish
List: Salmon, mackerel, sardines, trout, albacore tuna
Benefits in Mental Health:
Rich in omega-3 fatty acids, fatty fish reduce brain inflammation and improve communication between brain cells. This can lead to improved mood and reduced symptoms of depression.

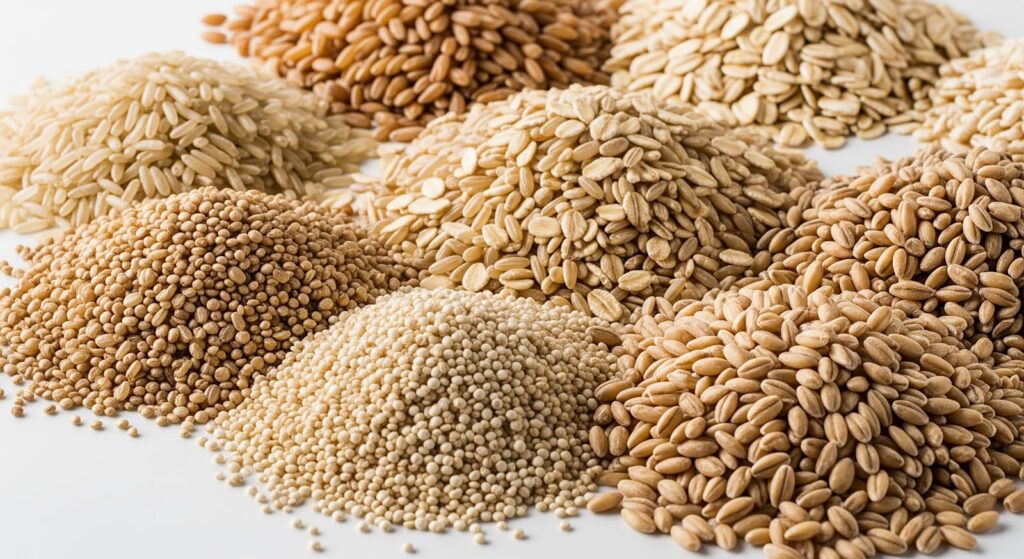
4. Whole Grains
List: Brown rice, quinoa, oats, barley, whole wheat bread, bulgur
Benefits in Mental Health:
Whole grains are slow-digesting carbohydrates that help stabilize blood sugar and reduce mood swings. They also support serotonin production—the “feel-good” chemical in the brain.

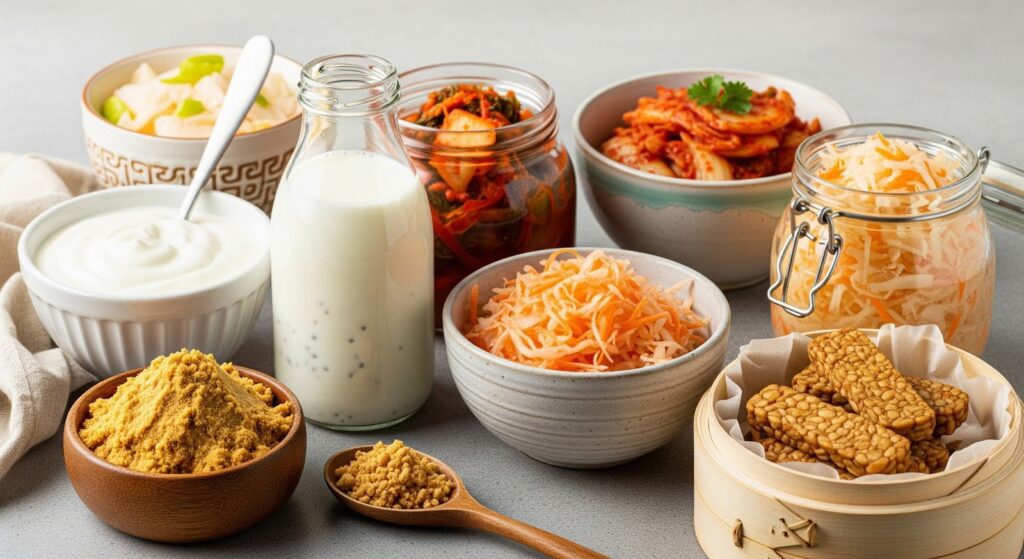
5. Fermented Foods
List: Yogurt with live cultures, kefir, kimchi, sauerkraut, miso, tempeh
Benefits in Mental Health:
These foods promote a healthy gut microbiome, which communicates with the brain via the gut-brain axis. A well-balanced gut is often linked to improved mood and reduced anxiety.

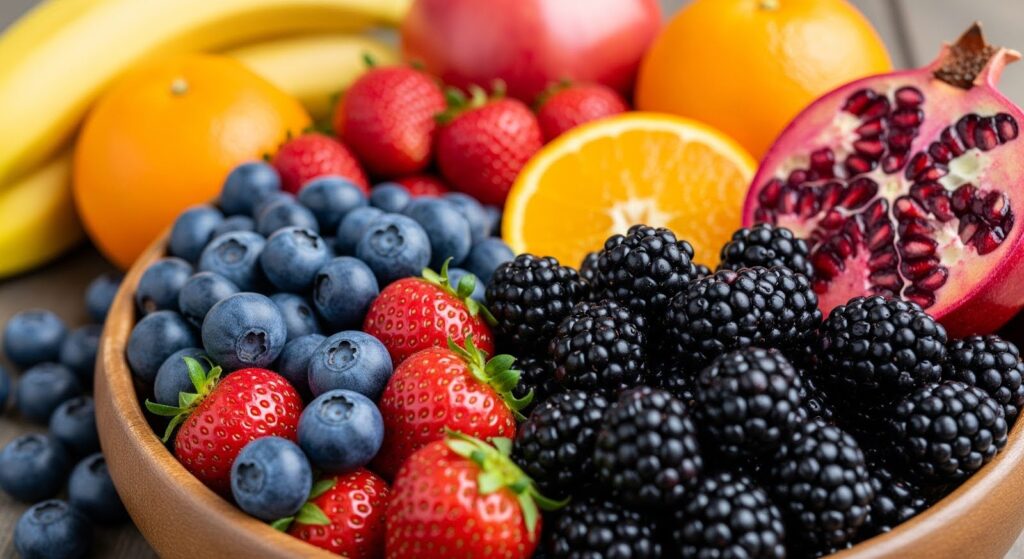
6. Berries and Colorful Fruits
List: Blueberries, strawberries, blackberries, oranges, pomegranates, bananas
Benefits in Mental Health:
Packed with antioxidants and vitamin C, berries protect the brain from oxidative stress. Bananas, in particular, are high in B6, which helps produce serotonin.

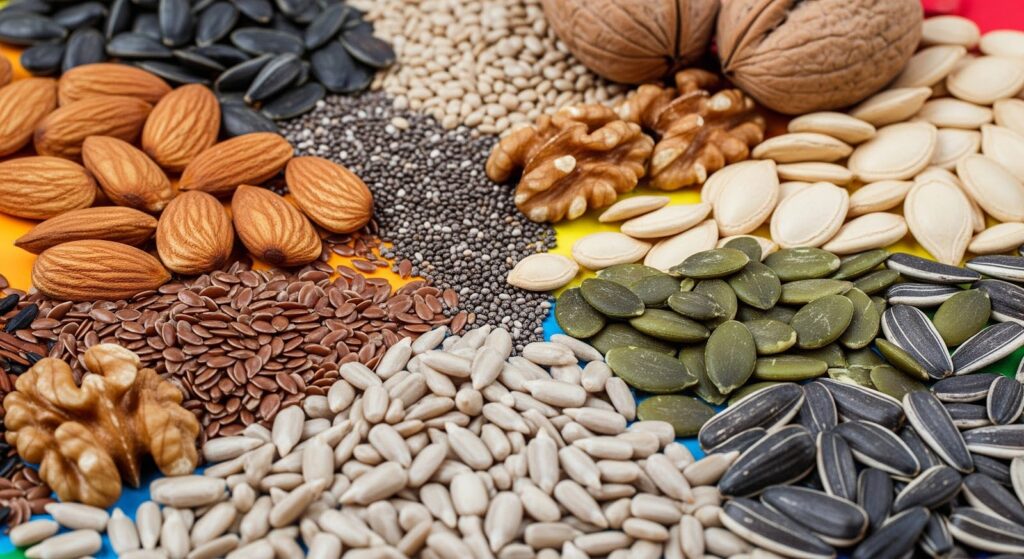
7. Nuts and Seeds
List: Almonds, walnuts, chia seeds, flaxseeds, pumpkin seeds, sunflower seeds
Benefits in Mental Health:
These are rich in healthy fats, zinc, selenium, and magnesium—nutrients known to reduce anxiety, improve memory, and support overall brain function.

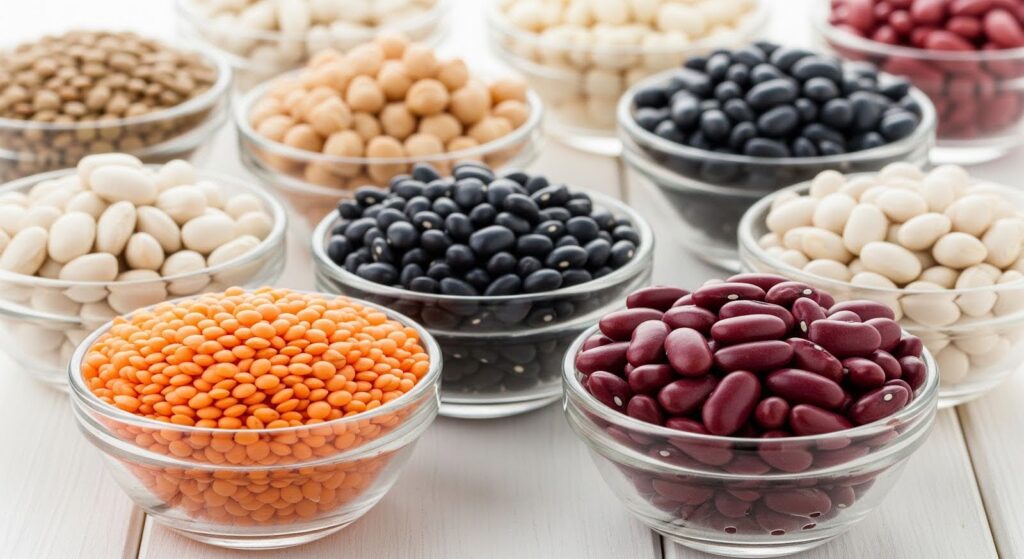
8. Legumes and Beans
List: Lentils, chickpeas, black beans, navy beans, kidney beans
Benefits in Mental Health:
High in fiber and folate, legumes support stable energy levels and neurotransmitter health. They also help regulate blood sugar and improve gut function.

Want guidance on building a mental-health-friendly diet? Meet with a Sage Health nutritionist or dietitian today.
Impact of Diet on Mental Health
How Diet Affects Mental Health
The impact of diet on mental health can be profound. The foods you eat affect your:
- Mood
- Memory
- Sleep quality
- Energy levels
- Stress response
- Risk for depression and anxiety
Here’s how it works:
- Nutrients like B vitamins, omega-3s, magnesium, and antioxidants directly influence neurotransmitter production and brain function.
- Processed foods high in sugar and unhealthy fats can increase inflammation and disrupt the gut microbiome, leading to mood instability.
- A poor diet can lead to nutrient deficiencies that affect cognitive performance, emotional resilience, and focus.
Even small changes, like replacing sugary snacks with a handful of nuts or adding leafy greens to dinner, can make a real difference in your mental clarity and emotional balance.
Strategies for a Healthy Diet for Mental Health
Not sure where to start? Try these easy habits to promote better emotional well-being:
- Eat the rainbow: Add colorful fruits and vegetables to every meal.
- Include protein at every meal: Helps regulate mood and avoid crashes.
- Snack smart: Choose nuts, seeds, or dark chocolate instead of sugary treats.
- Drink plenty of water: Hydration supports brain performance.
- Limit caffeine and alcohol: Too much can disrupt sleep and worsen anxiety.
- Minimize processed foods: Focus on whole, unprocessed ingredients.
Looking for personalized advice on what to eat for better mental health? Speak with a registered dietitian at Sage Health.
Final Thoughts: The Link Between Food and Mental Health
The link between food and mental health is clear: what you eat matters. A diet filled with whole, nutrient-rich foods can help reduce stress, balance mood, and support a sharper, more positive mindset.
For older adults, building healthy habits doesn’t have to be difficult. Sage Health is here to support you every step of the way—with compassionate care, expert nutritionists, and fitness and wellness services designed just for seniors.
Want to feel your best? Become a Sage Health patient today and take the first step toward a healthier, more balanced life.
Sources:
https://www.aetna.com/health-guide/food-affects-mental-health.html
https://www.mentalhealth.org.uk/explore-mental-health/a-z-topics/diet-and-mental-health